Introduction
evcc optimizes charging your electric vehicle with self-generated solar energy or low-cost electricity tariffs. The software works across manufacturers with hundreds of wallboxes, solar systems, and vehicles. evcc runs locally on a Raspberry Pi or NAS - no cloud required.
Learn how to install evcc on your hardware.
Functionality
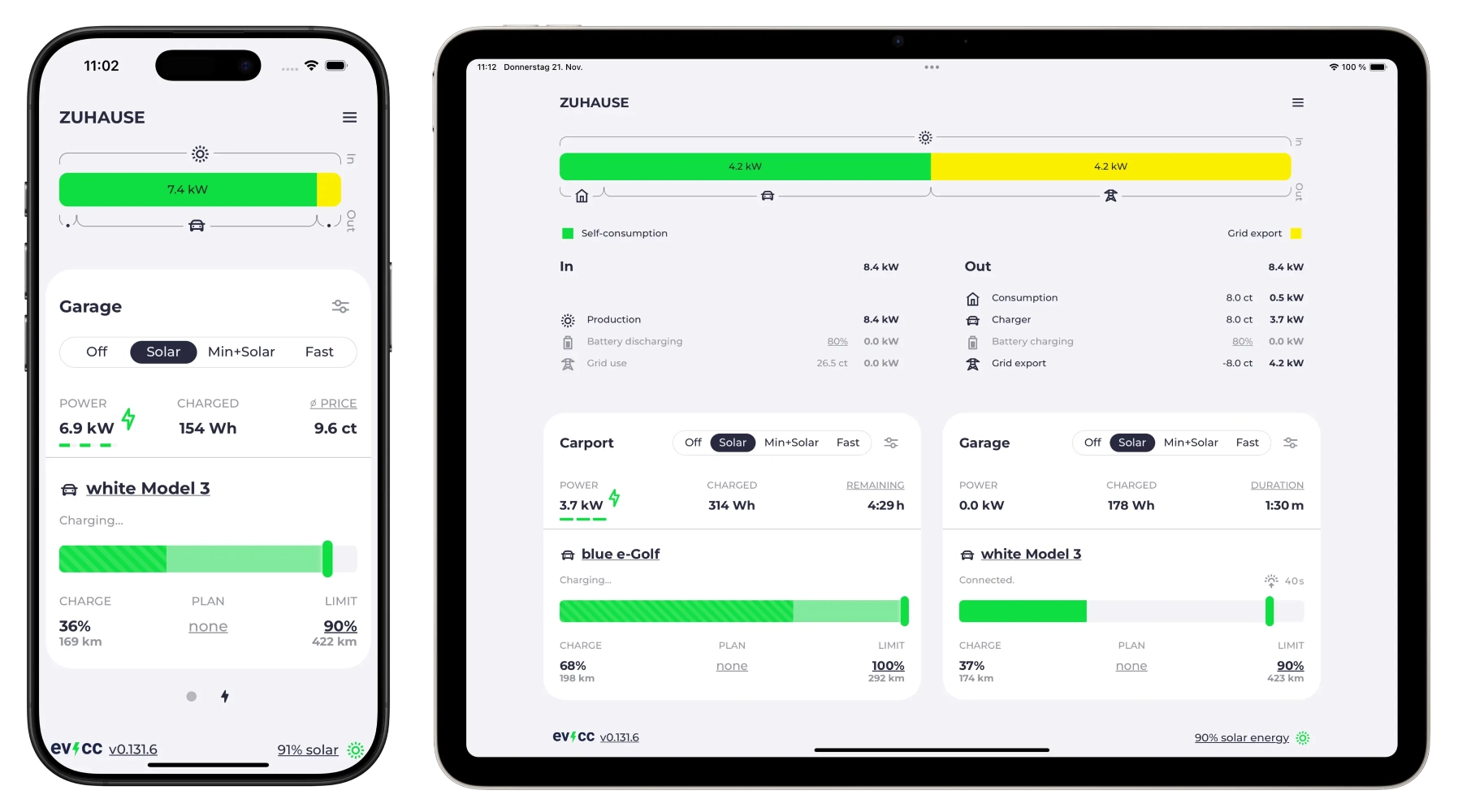
- Simple and clear User Interface
- Support for
- Plugins support a wide variety of wallboxes, meters, & vehicles over Modbus, HTTP, MQTT, JavaScript, Websockets, and Shell Scripts
- Status Notifications via Telegram, PushOver and many more
- Data Export via InfluxDB and Grafana
- Stepless regulation of charging flows with supported wall boxes (e.g the smartWB's OLC functionality)
- REST & MQTT APIs for integration into other home automation systems (such as Home Assistant)
Requirements
evcc requires at least the following:
- a supported Wallbox or Switchable Socket
- a supported Energy Meter at the house connection, or alternatively a supported solar inverter / other metering device that can measure current energy production
- a supported system to run evcc on!
Optionally:
- one or more supported Vehicles to collect charge status / level information
- additional supported Wallboxes or Switchable Sockets
- supported Solar inverter(s)
- supported Battery Storage System(s)
- a supported Energy Management System (such as SMA Sunny Home Manager)
- information on a dynamic electricity tariff
evcc comes without any kind of guarantee, and you use the software at your own risk. It is your responsibility to use evcc responsibly - it's your house fire!
Contact
- Support, configurations, questions about devices, and general discussion can be found in our Community Support Forum.
- We also have a Slack for development discussion.
Videos
Currently DE only (but please do suggest other languages!)
Kieler Open Source und Linux Tage 2024
Project update by Michael with a small focus on new features around dynamic electricity tariffs. Here are the slides for the presentation.
Night of open Knowledge 2023 in Lübeck Lecture
Michael gives an overview of the functionality and possibilities of evcc.
Here are the slides.
Linux Infotag 2023 Lecture
Michael introduces the project, talks about everyday work, and financing.
verdrahtet: Solar surplus with evcc (German)
Tackles evcc basics, integration with ioBroker, and integrating a homematic switch.
haus-automatisierung.com: Charging an Electric Vehicle with Solar Surplus (German)
Tackles evcc basics, custom plugins, control via MQTT and ioBroker, as well as different installation options.
smart home & more: Integrating evcc with Home Assistant (German)
Video series on setting up and using evcc with Home Assistant.
- Home Assistant: evcc Basisinstallation und Konfiguration
- Home Assistant: Schritt für Schritt - MQTT-Sensor mit Hilfe des MQTT-Explorer einrichten
- evcc-Daten nutzen: Effizientes Energiedashboard für Home Assistant
Articles
hobbyblogging.de
- Einführung in die Grundkonzepte: evcc - Was soll das sein?
- Einrichtung mit Balkonsolar und smarten Steckdosen: evcc installieren - So einfach geht's!
elefacts.de
- Grundlagen, Detaillierte Anleitung für Raspberry Pi Installation, Fernzugriff via Fritz!Box & DynDNS: evcc Anleitung für intelligentes PV Überschussladen mit vielen Wallboxen
- InfluxDB & Grafana: Von evcc erfasste Daten langfristig speichern und aufbereiten